Understanding Government Tenders
Government tenders are a key way for businesses to secure contracts with public sector organisations. They involve a competitive bidding process where companies propose solutions to meet specific needs.
This process ensures transparency, fairness, and value for money in the use of public funds. An organisation which receives the majority of it's funds from the public purse (government funding), will be classed as a contracting authority and have the following public procurement rules and obligations as though it is a government organisation.
Types of Government Bodies
- Central Government: This includes national government departments and agencies responsible for implementing national policies and managing specific sectors. Examples include:
- The Home Office: Manages immigration, security, and law and order.
- The Department for Education: Oversees education and children's services.
- Local Government: These are administrative bodies governing local areas, including county, district, and borough councils. They manage services such as:
- Manchester City Council: Responsible for local services like housing, social care, and waste collection.
- Cornwall Council: Manages regional services including transportation and environmental protection.
Public Sector vs. Government
While the terms "public sector" and "government" are often used interchangeably, there is a subtle difference:
- Government: Specifically refers to the administrative bodies (central and local) responsible for creating and enforcing laws.
- Public Sector: Encompasses all government bodies and other publicly funded organisations, such as:
- NHS (National Health Service)
- Universities and educational institutions: Publicly funded educational bodies.
Types of Government Tender Contracts
Government tender contracts come in several forms:
- Fixed-price: The supplier agrees to deliver for a set price
- Cost-reimbursement: The agency pays for all allowed expenses plus a fee
- Time and materials: Payment is based on hourly rates and material costs
Other common types include:
- Indefinite delivery: For repeated orders over time
- Sealed bid: Suppliers submit secret bids, with the lowest often winning
- Negotiated: Allows for discussion and changes during the process
Each type suits different project needs. Fixed-price works well for clear, defined tasks. Cost-reimbursement fits complex projects with uncertain scopes. Choosing the right contract type is crucial for both the government and suppliers.
Government Tenders: Example Bodies - Contracting Authorities
Type of Contracting Authority | Organisation Examples | Example Government Tenders |
|---|---|---|
Central Government | Home Office, Ministry of Defence | National security projects, defence equipment procurement |
Local Government | Manchester City Council, Cornwall Council, Camden Borough Council | Local infrastructure maintenance, waste collection services |
Emergency Services | London Fire Brigade, Greater Manchester Police | Firefighting equipment, emergency response vehicles |
Public Health | NHS England, Public Health Wales | Medical equipment and supplies, public health campaigns |
Education | University of Oxford, Manchester Metropolitan University | Construction of educational facilities, research grants |
Housing | Clarion Housing Group, Peabody Trust | Social housing development, maintenance services |
Transportation | Transport for London, Network Rail | Public transportation systems, rail infrastructure projects |

Eligibility for Government Tenders
Qualifying for government tenders involves meeting specific requirements and standards. Companies must demonstrate their capabilities, financial stability, and compliance with regulations to be considered for public sector contracts.
Essential Qualifications
To bid for gov tenders, businesses need to meet basic eligibility criteria. These often include:
- Legal status: Must be a registered company or organisation
- Financial stability: Proof of sound financial health
- Experience: Relevant track record in the industry
- Capacity: Ability to deliver the required goods or services
- Compliance: Adherence to tax, insurance, and legal obligations
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can also compete for contracts. Many tenders have specific provisions to encourage SME participation.
Assessment Criteria
Contracting authorities evaluate bids based on various factors:
- Technical competence
- Quality of proposed solution
- Value for money
- Innovation and sustainability
- Risk management
- Social value contribution
Each tender will outline its specific evaluation criteria. Bidders should carefully review these and tailor their proposals accordingly.
Certifications and Standards
Certain certifications and standards may be required or preferred for gov tenders:
- ISO certifications (e.g., ISO 9001 for quality management)
- Industry-specific accreditations
- Health and safety certifications
- Environmental management standards
- Cyber security certifications (e.g., Cyber Essentials)
Meeting these standards can give bidders a competitive edge. It's important to keep certifications up-to-date and be prepared to provide evidence of compliance during the bidding process.
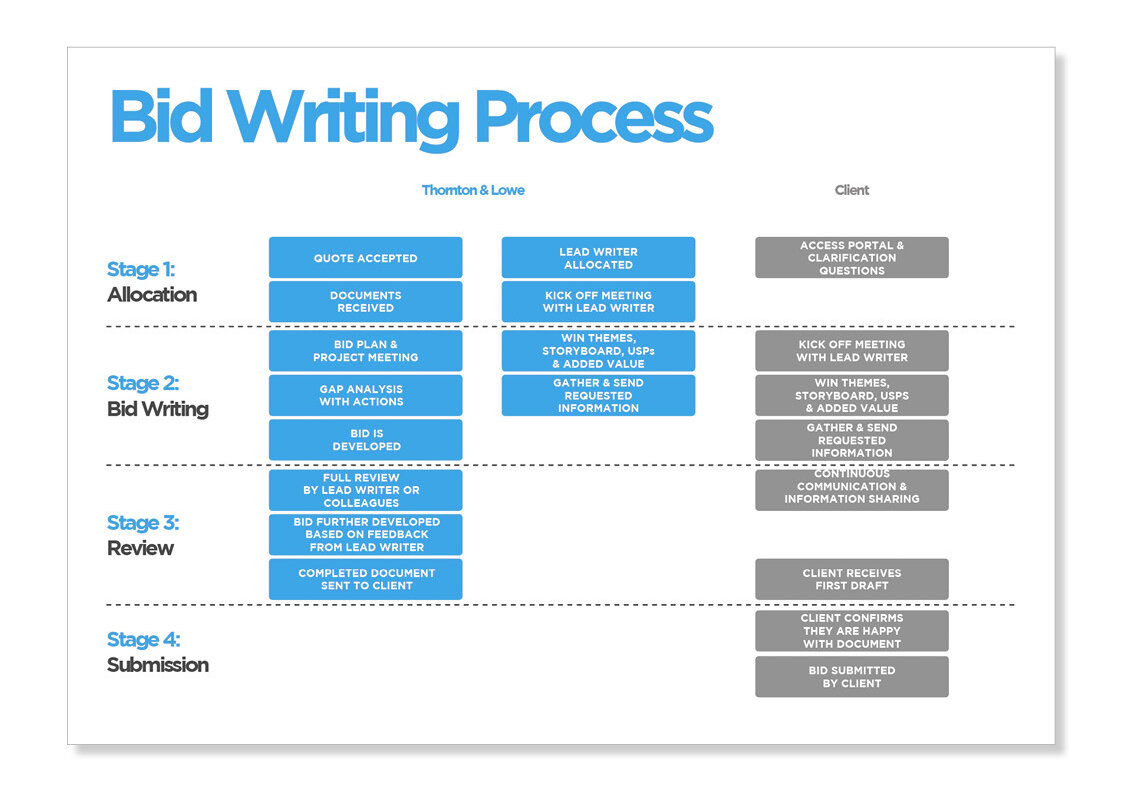
The Bid Writing Process for Government Contracts & Tenders
Writing a strong bid for government tenders requires careful planning and execution. A well-crafted proposal can make the difference between winning and losing a contract.
Planning and Preparation
The first step is to understand the tender requirements. Read the documents carefully and note key deadlines, evaluation criteria, and submission guidelines. Research the contracting authority to grasp their needs and priorities.
Create a bid/no-bid checklist to decide if the opportunity is right for your business. Consider factors like project scope, budget, and competition.
If bidding, assemble your team and assign roles. Gather supporting documents such as financial statements, certifications, and case studies. Set up a timeline with milestones to keep the process on track.
Develop your win strategy. Identify your unique selling points and how they align with the buyer's needs. Plan how to address potential weaknesses or risks in your bid.
Structuring the Response
Break down the tender into sections and create an outline. Follow the structure provided in the tender documents closely.
Start with an executive summary that highlights key points and demonstrates your understanding of the project. Use clear headings and subheadings to organise information logically.
Answer each question directly and thoroughly. Back up claims with evidence and examples. Use visuals like charts or diagrams to illustrate complex ideas.
Ensure consistency in formatting, tone, and messaging throughout the document. Cross-reference sections to show how different parts of your proposal fit together.
Tips for Persuasive Writing
Use simple, clear language. Avoid jargon unless specifically required. Write in short sentences and paragraphs for readability.
Focus on benefits to the buyer, not just features of your product or service. Show how you'll solve their problems or meet their goals.
Be specific. Use numbers, statistics, and concrete examples to support your claims. Avoid vague statements or promises.
Proofread carefully for errors. Ask someone not involved in writing to review the bid for clarity and impact.
Tailor your writing style to the audience. A technical bid may need more detail, while a management summary should be concise.
You may also like:
Need advice?
Contact us todayFinancial Considerations
Bidding for government tenders requires careful financial planning and risk management. Crafting a competitive yet profitable proposal involves strategic costing and pricing approaches. It's also crucial to assess and mitigate potential financial risks.
Costing and Pricing Strategies
When bidding for government tenders, accurate costing is key. Start by breaking down all project expenses, including labour, materials, and overheads. Use historical data and market research to estimate costs precisely and ensure you use any pricing schedules provided.
Consider the following pricing approaches:
- Cost-plus pricing: Add a markup to your total costs
- Value-based pricing: Set prices based on the perceived value to the client
- Competitive pricing: Align your bid with market rates
Factor in potential cost fluctuations over the contract period. Build in some flexibility to account for changes in labour or material costs.
Financial Risk Management
Gov tenders often involve substantial financial commitments. Identify potential risks such as project delays, cost overruns, or payment issues. Create contingency plans for each scenario.
Some risk management strategies include:
- Setting aside a contingency fund (typically 5-10% of the total bid)
- Negotiating favourable payment terms
- Using financial instruments like performance bonds

Quality Assurance in Bids
Quality assurance plays a vital role in crafting winning government tenders. It ensures bids meet all requirements and showcase a company's strengths. Proper quality control and evidence of past performance are key elements.
Implementing Quality Control
Quality control in bid writing involves careful checks at each stage. A thorough review of the tender documents is essential. This helps identify all criteria and requirements.
Creating a bid checklist is useful. It should cover all needed elements and deadlines. Having multiple team members review the bid helps catch errors.
Proofreading is crucial. Spelling, grammar, and formatting mistakes can harm credibility. Using tools like spell-checkers can help, but human review is still needed.
Double-checking all figures, dates, and claims is important. Inaccurate information can disqualify a bid.
Evidence of Past Performance
Showing proof of past successes strengthens a bid. This builds trust with the evaluators. Include details of similar projects completed on time and within budget.
Customer testimonials add credibility. Choose quotes that highlight key strengths related to the tender.
Case studies can showcase problem-solving skills. Describe challenges faced and how they were overcome.
Quantifiable results are powerful. Use statistics to show improvements or savings achieved.
Including awards or certifications can set a bid apart. These prove industry recognition of quality work.

Legal and Ethical Compliance
Bidding for government tenders requires strict adherence to legal regulations and ethical standards. Firms must navigate complex regulatory requirements while upholding integrity throughout the process.
Regulatory Requirements
Government tenders are subject to specific laws and regulations. Bidders must comply with procurement rules set by the Public Contracts Regulations 2015. These rules cover fair competition, transparency, and non-discrimination. Most recently the Procurement Act.
Firms need to register on official procurement portals like Contracts Finder. This helps them access tender opportunities and submit bids properly.
Data protection is crucial. Companies must follow GDPR guidelines when handling personal information in tender documents. Failure to do so can lead to disqualification or legal issues.
Bidders should be aware of sector-specific regulations. For example, construction tenders may require adherence to building codes and safety standards.
Maintaining Ethical Standards
Ethical conduct is vital in government tendering. Firms must avoid conflicts of interest and disclose any potential issues upfront.
Bribery and corruption are strictly forbidden. Companies should have clear anti-bribery policies in place and train staff on ethical practices.
Honesty in bid submissions is non-negotiable. Exaggerating capabilities or providing false information can result in bid rejection and legal consequences.
Fair competition is key. Collusion with other bidders or attempts to manipulate the process are illegal and can lead to severe penalties.
Firms should maintain accurate records of all tender-related communications and decisions. This promotes transparency and helps in case of audits or disputes.
Speak with a gov tendering expert
Contact usStrategic Partnerships and Alliances
Forming strategic partnerships can greatly boost a company's chances of winning government tenders. These collaborations allow firms to combine strengths, share resources, and tackle larger projects.
Collaborations
Partnerships let businesses fill skill gaps and offer more complete solutions. A small IT firm might team up with a larger consultancy to bid on a big tech project. This gives the small company access to more resources and expertise.
Joint ventures are common in construction tenders. A builder could partner with an architect and engineer to offer end-to-end services. This makes the bid more appealing to government buyers looking for comprehensive solutions.
Partnering also spreads financial risk. Companies can share costs of bid preparation, contract delivery, and any potential losses.
Consortium Bidding
Consortiums bring together multiple firms to bid as one entity. This approach works well for complex, high-value tenders that need diverse skills.
A consortium might include:
- A lead bidder to manage the contract
- Specialist firms for niche areas
- SMEs to meet diversity targets
- Local partners for regional knowledge
Consortiums must agree on roles, profit sharing, and risk management upfront. Clear governance is key to avoid disputes during delivery.
Government buyers often favour consortium bids. They reduce procurement complexity and offer 'one throat to choke' for contract management.

Post-Submission Considerations
After submitting a government tender bid, key factors come into play. These include how bids are assessed and ways to learn from the process for future opportunities.
Evaluation Process
Government departments use set criteria to review bids. They look at factors like price, quality, and ability to deliver. A panel often scores each bid against the tender requirements. Technical experts may check if proposed solutions meet specifications. Financial teams assess if costs are realistic and offer value for money.
The evaluation can take weeks or months depending on the contract size. During this time, bidders should be ready to answer any questions. Evaluators might ask for more details or clarifications. It's important to respond promptly and thoroughly.
Some contracts have multiple stages. Bidders who make the shortlist may need to give presentations or attend interviews. This lets evaluators dig deeper into proposals and meet key team members.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Whether successful or not, getting feedback is crucial. Government buyers should offer debriefs to explain their decision. These sessions highlight a bid's strengths and weaknesses. Smart bidders use this info to refine future proposals.
Key questions to ask include:
- How did the bid score against criteria?
- What areas need improvement?
- Were there any misunderstandings?
It's wise to keep records of all feedback. This helps spot patterns and track progress over time. Many firms create 'lessons learned' logs after each bid. These capture insights to apply in upcoming tenders.
Some organisations hire bid writing experts to review past submissions. These professionals can spot common mistakes and suggest ways to boost win rates.

Using Technology in Bid Writing for Government Tenders
Technology plays a key role in modern bid writing. It helps streamline processes and boost efficiency when responding to government tenders.
Bid Management Software
Bid management software helps organise the bid writing process. It stores important documents and tracks deadlines. Many tools offer templates for common bid sections. This saves time and ensures consistency.
Some software can analyse past bids. It highlights successful approaches to reuse. Advanced systems use AI to suggest improvements to bid text. They can check for compliance with tender requirements too.
Cloud-based platforms allow team collaboration. Multiple writers can work on different sections at once. Managers can easily review progress and provide feedback.
Innovation in Responding to Tenders
New bid software is changing how companies respond to tenders. Data visualisation tools create compelling graphics. These help explain complex ideas quickly. Interactive dashboards let evaluators explore project data. Automated proposal generators use AI to draft responses. They pull from company databases and past bids. Human writers then refine the content.
Mobile apps allow bid teams to work on the go. They can update status, share files, and communicate easily.
Need bid support?
Contact us todayFrequently Asked Questions
Government tender bidding involves several key steps and strategies. Understanding the process and requirements is crucial for success.
What steps are involved in the preparation of a bid for a government tender?
The preparation of a government tender bid typically involves:
- Carefully reviewing the tender documents
- Gathering all required information and supporting materials
- Drafting responses to each section of the tender
- Checking compliance with all specifications
- Calculating accurate pricing
- Proofreading and reviewing the entire submission
How can one begin the process of bidding on government contracts within the UK?
To start bidding on UK government contracts:
- Register on relevant procurement portals like Contracts Finder
- Set up alerts for tenders in your industry
- Ensure your business meets eligibility requirements
- Begin with smaller contracts to gain experience
- Consider partnering with more established companies initially
What are the key components of a successful tender submission?
A strong government tender submission should include:
- Clear and concise responses to all questions
- Evidence of your company's capabilities and experience
- A competitive pricing structure
- Compliance with all tender specifications
- High-quality, professional presentation
Where can one find listings for upcoming government tenders in the UK?
UK government tenders can be found on:
- Contracts Finder (for contracts over £10,000)
- Find a Tender (for higher value contracts)
- Individual government department websites
- Local council procurement portals
- Industry-specific tender listing services
- Tender Pipeline is our free tool, which collates opportunities from all those listed above
What strategies could enhance the effectiveness of bid writing for government tenders?
Effective bid writing strategies include:
- Thoroughly addressing all selection criteria
- Using clear, concise language
- Providing specific examples and evidence
- Highlighting your unique selling points
- Tailoring your bid to the specific requirements of each tender
Which online resources provide guidance and examples for government tender bid writing?
Useful online resources for government tender bid writing include:
- Gov.uk procurement policy guidance
- Crown Commercial Service website
- National Audit Office best practice guides
- Industry association websites and forums
- Professional bid writing consultancy blogs and resources, like this one!



