Talk to us 01204 238 046
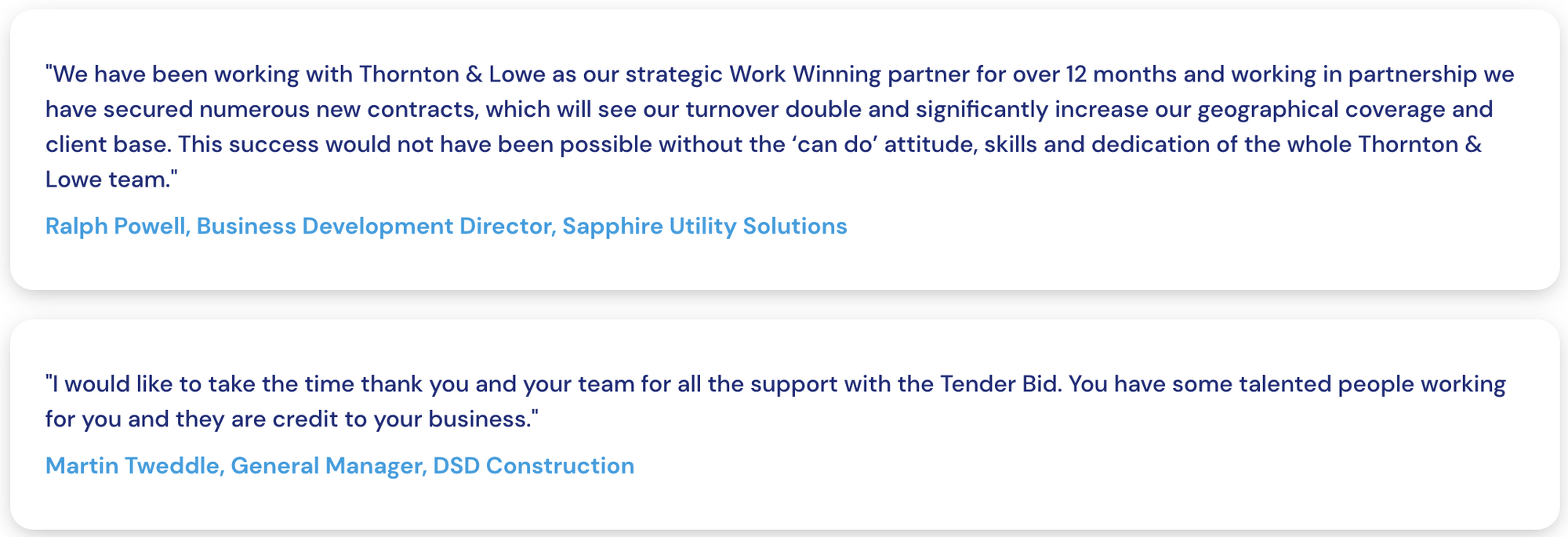
Over 75% success rate!
Push your business to the next level!
Procurement compliance, contract management & value for money services
Taking the stress out of organising your current bids and planning your pipeline
Helping you to produce a comprehensive and compliant CRP
Our specialist bid recruitment division
Stand out from the competition
Access Tender Library, Tender Pipeline or Book a Demo
Finding tenders that suit your business
Partner with us to improve your bid output
A range of standard Bid Templates, produced by our experts for your sector
Content creation that drives qualified leads
Writing a strong method statement for a tender submission shows a buyer that you've thought through how you'll complete a job. This guide will show you how to avoid common mistakes and write a method statement that really impresses.
A method statement in tender submissions is a document that outlines how you will carry out a specific task safely and efficiently. That's it!
Typically, required as part of health and safety requirements and tendering. At its core a method statement is a tool for planning and communicating work procedures. It needs to ensure compliance with relevant laws and be reflective of how you deliver your service. Once developed and in place for your business - it becomes a key tool for training, monitoring and quality, as well as evidence of your approach, which you may need to share with clients.
The H&S method statement will be updated as the business develops, improves and laws and best practices get updated. Tender method statements will change a lot more though! As these tender method statements are often another term for tender or ITT procurement questions. Each response, for each tender should be unique - or certainly tailored from a base of how you do things.
A method statement describes the steps needed to complete a job safely. It lists the risks involved and the safety measures to control them. The main purpose is to protect workers and others from harm.
Method statements help:
• Plan work in advance
• Identify potential hazards
• Set out safety precautions
• Explain the task to workers
• Meet legal health and safety requirements
They're often used with risk assessments. Together, these documents form a safe system of work. Good method statements can improve productivity and quality too.
Method statements are widely used in high-risk industries. The construction sector relies on them heavily. Other fields that often need method statements include:
• Manufacturing
• Engineering
• Utilities
• Facilities management
• Event planning
In construction, you might need a method statement for tasks like demolition work. In manufacturing, it could be for operating machinery. Utility companies use them for repairs and installations. Any job with significant risks should have a method statement. This helps keep workers and the public safe.
Within the context of a tender or ITT, you will likely have to supply relevant health and safety related method statements and risk assessments as evidence. However, method statements is also the common term used within procurement to describe quality tender questions.
When answering tender questions, a well-written method statement is crucial for winning tenders. It shows your understanding of the project, your approach, and your commitment to safety and quality.
The foundation of an effective method statement begins with thorough research and preparation. Before putting pen to paper, take time to carefully review all tender documentation, paying particular attention to specific requirements, evaluation criteria, and the client's stated objectives.
Understanding exactly what the client values will allow you to emphasise the aspects of your approach that will resonate most strongly with evaluators.
Once you have a clear understanding of the requirements, structure your response in a way that makes evaluation straightforward. Create a logical flow that mirrors the sequence of the tender questions or project phases. This not only demonstrates your organisational skills but also makes it significantly easier for evaluators to find and score the information they need.
When detailing your methodology, clarity is paramount. Explain your approach in plain language, breaking down complex processes into clear, sequential steps that anyone could follow. Be precise about how you will deliver each aspect of the project. Vague assurances will not win tenders, but detailed explanations of your processes will build confidence in your capability.
Your method statement must include essential information such as project details, resource allocation, and timelines. These elements should be presented with specific detail, not general statements.
For example, avoid simply stating that qualified staff will be assigned. Name key personnel and outline their relevant experience and qualifications. Similarly, when discussing timelines, include specific milestones and explain how you will ensure deadlines are met, even if challenges arise.
The most compelling method statements are specific and measurable. Rather than making broad claims about quality or efficiency, provide concrete metrics and detailed procedures.
This might include:
The frequency of quality inspections
The specific checklists used
The response times for addressing issues
This level of detail shows that you have thought through how to deliver the project and already have systems in place to manage it effectively.
Supporting your methodology with evidence significantly strengthens your credibility. Reference previous projects where you have successfully implemented similar approaches, and include the outcomes achieved.
If you hold relevant certifications or accreditations, explain how these underpin your methodology and provide additional assurance to the client. This evidence-based approach transforms your method statement from a theoretical explanation into a practical demonstration of how you work.
Visual elements can turn a dense method statement into a more accessible and memorable document. Flowcharts, diagrams, or tables can help clarify decision-making, illustrate your delivery approach, or summarise processes.
Well-designed visuals not only improve understanding but also show your ability to communicate complex information clearly, which is a valuable quality in contract delivery.
Before submitting your method statement, have both technical experts and bid specialists review it. Technical reviewers can check for accuracy and completeness, while bid professionals can ensure your response aligns with the evaluation criteria and presents your offer in the best possible way.
This dual review process gives your submission the best chance of scoring well.

In the context of tenders, it’s common to be asked for both Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and Method Statements. While they may appear similar, they serve different purposes.
A Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) outlines how your organisation carries out a routine task. It’s used to show consistency, ensuring that all staff follow the same process regardless of who’s delivering it. SOPs are often organisation-wide and don’t usually reflect the specific details of a project.
In contrast, a Method Statement is written specifically for the project or contract you are bidding for. It explains how you will deliver a particular activity on that job, often with a strong focus on health and safety, compliance, and risk management. In construction and other high-risk sectors, Method Statements are used to show the client that you’ve thought through the detail and can carry out the work safely and to the required standards.
When responding to a tender, your SOP might be included as supporting evidence, while your Method Statement should be tailored to the project itself. Understanding the difference is important if you want to answer the question fully and meet the buyer’s expectations.
Thornton & Lowe can help businesses write effective method statements as part of their bid writing and bid management services. As a bid writing consultancy, we have a team of technical bid writers and bid managers who have worked on hundreds of tenders and proposals that include method statements each year.
Our extensive experience in bid writing allows us to assist clients in creating clear, concise, and compelling method statements that are essential components of successful bids. We understand that a method statement describes the steps needed to complete a job safely, lists the risks involved, and outlines the safety measures to control them.
If your business needs support in writing method statements as part of a bid or tender submission, contact us today - hello@thorntonandlowe.com / 01204 238046.
A method statement contains several common and important elements:
The title and purpose section sets the stage for the entire method statement. It clearly identifies the specific task or project being addressed. This part should include:
The purpose outlines the main objectives and goals of the task. It explains why the work is necessary and what it aims to achieve. This helps workers understand the importance of their role in the overall project.
Scope of Work
The scope of work defines the boundaries of the task. It outlines:
This section helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures all parties have a clear understanding of the work to be done. It may also mention any relevant standards or regulations that must be followed.
This is the heart of the method statement. It breaks down the task into logical, manageable steps. Each step should be:
Use bullet points or numbered lists to make the steps easy to read. Include any specific techniques or methods to be used. If certain steps require extra care or attention, highlight them.
Safety is paramount in any project. This section identifies potential hazards and outlines measures to mitigate risks. It should include:
Be specific about safety protocols. For example, "Wear safety goggles when using power tools" is better than "Use appropriate PPE".
List all the tools, materials, and equipment needed to complete the task. This might include:
Specify any certifications or inspections required for equipment use. Include details on proper storage and handling of materials.
This section outlines who will be involved in the task and what their roles are. Include:
Clearly defining roles helps prevent confusion and ensures everyone knows what's expected of them.
Explain how the work will be monitored and reviewed to ensure it meets the required standards. This section should cover:
Include any specific quality standards that must be met. Outline the process for addressing and correcting any issues that arise during the work.

Templates and best practices can streamline the process of creating effective method statements. They help ensure you include all crucial elements while avoiding common mistakes.
Method statement templates provide a structured framework for organising key information. They typically include sections for:
Using templates can significantly reduce the time needed to create a method statement. They ensure you don't overlook important details and maintain consistency across projects.
To get started, choose a template that aligns with your industry and project type. Customise it to fit your specific needs, adding or removing sections as necessary.
When crafting method statements, be aware of these common mistakes:
To avoid these pitfalls, use clear, concise language and provide specific details for each step. Regularly review and update your method statements as the project progresses.
Involve team members and subject matter experts in the creation process. Their input can help identify potential issues and ensure all aspects of the task are covered.
To tailor a template to your specific needs:
Adapt the risk assessment section to address the unique hazards of your project. Be thorough in outlining safety measures and emergency procedures.
Remember to keep your customised template flexible. You may need to adjust it further as you use it for different projects or tenders.
In tender documents, especially for construction and related sectors, you may come across the phrase ‘Method of Statement’ used as a heading for a quality response. While the original term comes from health and safety documentation, in procurement it now often refers to your full explanation of how you plan to deliver the work.
This use of the term usually appears in ITT quality questions asking you to describe your methodology, timelines, risk management, and team structure. Buyers want to see both the practical steps you’ll take and how those actions fit into a wider project strategy.
Treat it as your opportunity to explain how the job will run in real terms. The better you can show control, planning, and safety awareness, the stronger your response is likely to score.
If you’re preparing this as part of a tender response, you can refer to our detailed guide above on how to write a project-specific Method Statement that meets client expectations.
Project Title: | XX Construction Phase X |
Company: | Company X |
Address: | 123 Lane... |
Project/Task: | To refurbish... |
Location: | Bolton |
Project/Task Number (if applicable): | XXX |
Risk Assessment (RA) Number (if applicable): | XXX |
RA Date: | XXX |
Method Statement (MS) Number (if applicable): | XXX |
MS Date: | XXX |
Project/Task Description: | Provide a concise overview of the task and its anticipated duration. |
Known Hazards: | List hazards identified in the risk assessment, including those arising from the task's proximity to other activities. |
Responsible Person(s): | Names and contact details of individuals overseeing the task. |
Planning and Preparation | |
Monitoring: | Describe how health, safety, and environmental performance will be monitored. Confirm workers' awareness of the incident reporting process. |
Operational Sequence: | Outline the step-by-step procedure for safe task execution, incorporating risk assessment controls. |
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): | Specify required PPE, ensuring it aligns with identified hazards. |
Permits: | List any necessary permits or authorisations (e.g., hot work permits, confined space entry permits). |
Labour: | Detail the competency and qualifications of the personnel involved. |
Plant/Equipment: | List equipment to be used, highlighting safe working practices, statutory checks, and relevant operator training. |
Materials: | Identify materials, addressing potential safety issues (manual handling, storage, disposal). |
Deliveries: | Specify routes and drop-off locations. |
Safety and Emergency Procedures | |
Emergency Arrangements: | Outline first aid, fire, and other emergency procedures, including first aider names and equipment locations. |
Environmental Issues: | Detail controls for emissions to air, water, and land. |
Approvals and Briefings | |
Prepared By: | Name, Date, Position, Signature |
Reviewed By: | Name, Date, Position, Signature |
Attachments: | List any attached documents (e.g., sketches, certifications, risk assessments). |
Method Statement Briefing Record | |
Briefing Delivered By: | |
Date: | |
Attendees: | (Signatures and printed names) |
The following table provides a structured guide for completing a tender method statement, including sections for answering method statement questions, indicating word count, and adding relevant evidence. This template can help you provide clear, structured answers while ensuring you meet the tender requirements and address social value elements.
Section | Question | % Weighting | Word Count | Answer/Response | Evidence to Include |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Project Overview | What is the project's purpose and objectives? | 10% | 200 words | Outline the project’s goal, location, duration. | Contract scope, project timelines, client brief. |
Scope of Work | How will the work be carried out? | 20% | 300 words | Break down tasks, key stages, and methodologies. | Work plan, method diagrams, previous project examples. |
Risk Assessment & Safety | How will you ensure a safe working environment? | 15% | 250 words | Identify risks and safety measures, including PPE. | Risk assessments, safety certifications, staff safety training records. |
Resource Allocation | What resources will be used for the project? | 10% | 200 words | List personnel, materials, and tools needed. | Staff qualifications, equipment lists, resource schedule. |
Quality Assurance | How will you maintain quality throughout? | 15% | 250 words | Detail inspection routines, standards, and testing. | QA plan, inspection checklists, material quality certifications. |
Social Value | How will you deliver social value through the project? | 20% | 300 words | Detail plans for local employment, sustainability, and community engagement. | Local hiring commitments, environmental policies, training schemes, community sponsorships. |
Timeline & Phasing | What is the project timeline? | 10% | 150 words | Provide the breakdown of phases and completion dates. | Gantt chart, project milestones, key deadlines. |
Health & Safety Protocols | What emergency protocols will be in place? | 5% | 100 words | Describe procedures for handling emergencies. | Emergency response plan, staff emergency training. |
This template ensures that each key area of the tender method statement is addressed clearly and concisely, helping your bid stand out while complying with the tender's requirements.
Transitioning from traditional paper-based documents to digital platforms allows you to work more efficiently and in a format which clients increasingly require!
Our Tender Library software uses your template method statement answers - allow you to find them quickly and tailor quickly using AI (if you prefer). It not only provides a robust repository of previous method statements but also helps you maximise the performance of your existing documents. With Tender Library, you can:
Explore more about our Bid Management Software here.
A method statement is a document that explains how a specific task will be carried out safely and efficiently. It’s often required in tenders and high-risk industries such as construction. It outlines the steps involved, safety measures, responsibilities, and any equipment or materials needed.
Start by reviewing the tender documents carefully. Then explain your project approach step-by-step, focusing on how you'll deliver the service, manage risks, ensure quality, and meet the client's specific requirements. Tailor each method statement to the opportunity — don’t copy and paste a generic one.
A Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) outlines how to carry out routine tasks consistently across an organisation. A method statement, on the other hand, is written for a specific project or contract. It shows how a task will be done safely and to the required standard for that particular job.
Yes. A method statement template can help you structure your approach clearly and consistently. It usually includes sections like project details, scope of work, step-by-step instructions, risk assessment, resources needed, and health and safety measures. Templates should always be adapted to match the specific tender or task.
Yes, method statements are commonly required for construction tenders. They show how you’ll complete the work safely, meet regulations, and manage delivery. Even if not explicitly requested, including one can strengthen your bid by demonstrating control, planning, and professionalism.
Made by Statuo



