Talk to us 01204 238 046
Over 75% success rate!
Push your business to the next level!
Procurement compliance, contract management & value for money services
Taking the stress out of organising your current bids and planning your pipeline
Helping you to produce a comprehensive and compliant CRP
Our specialist bid recruitment division
Stand out from the competition
Access Tender Library, Tender Pipeline or Book a Demo
Finding tenders that suit your business
Partner with us to improve your bid output
A range of standard Bid Templates, produced by our experts for your sector
Content creation that drives qualified leads
This guide will show you how to write a mobilisation plan as part of a tender response. It will explain what a mobilisation plan is and when to use it, as well as providing an example of how to structure your plan. Our aim is to help you to write detailed, practical plans that contribute towards a winning bid. For further help, get in touch with our team today.
Get support for your planThe first hint is in the name: a mobilisation plan revolves around organising, planning and getting ready to take action. It's a wider strategy that details the specific steps and resources needed to start a project.
In the context of tendering, a mobilisation plan is used to ease the transition from the bidding stage to the actual work (the delivery). With this in place, you can ensure that everything is ready to go when the project begins.
A mobilisation plan includes:
If you're taking over from another organisation, then your mobilisation plan may also cover TUPE. For many service businesses, this can be a key element of taking over and preparing for a new contract.
Having a good mobilisation plan helps to prevent problems and delays, and makes sure everyone is on the same page and ready for the challenges of the project.
Importantly, though, a good mobilisation plan is crucial for your chances of winning a contract in the first place. A mobilisation tender question can be worth 20% of the overall score. So, it's important to get it right!
At Thornton & Lowe, we help our clients to write detailed, structured mobilisation plans, as well as offering help with supporting evidence and quality and social value questions.
A mobilisation plan is an important part of:
Mobilisation plans are especially important when writing bids or responding to tenders. Often, the tender process will ask bidders to include a detailed mobilisation plan in their proposal. This shows that the bidder understands what the project needs and is ready to start working right away if they win the contract.
When writing a bid, the mobilisation plan should be customised to fit what the client wants, as described in the tender documents. This means looking closely at the project, figuring out potential risks and challenges, and coming up with ways to solve them. The plan should also highlight the bidder's skills, resources, and experience in successfully completing similar projects before.
In short, a mobilisation plan is an essential tool for making sure projects, contracts, and business expansions start and run successfully. It's particularly crucial when writing bids and responding to tenders, where a strong mobilisation plan can set a bidder apart from the rest and show their ability to deliver the desired results.
When developing a mobilisation plan, you will need to define the scope, objectives and deliverables of your project. While you're likely to start with a template covering your key tasks, the plan itself should be tailored to the client's requirements.
Remember to base your plan on the practical steps required in order to prepare to deliver a contract. Ensure that it is specific to the client's needs rather than offering boilerplate responses.
Pulling in specific elements from the tender requirements as additional stages in your mobilisation plan can really help. As well as making sense from a practical point of view, doing so shows that you've considered the client's needs. If the client expects weekly meetings in the early stages, for example, then you need to make sure that this is included. This helps you to both plan out your time and builds trust.
Mobilisation is particularly critical for construction projects. That's because they tend to be complex, often including site preparation, equipment delivery, and safety protocol implementation.
The mobilisation process typically involves:
Your project mobilisation plan should be comprehensive yet flexible. It serves as a roadmap for the initial stages of your project.
Key elements of a strong mobilisation plan include:
When limited to providing a single document as a mobilisation plan, the best route can be to create an Excel spreadsheet. This can contain additional tabs for key tasks and risk management, as well as including Gantt charts.
Get help writing a mobilisation plan from the experts at Thornton & Lowe.
Contact us todayIf you're new to bidding, you might not know how to start writing a detailed mobilisation plan. The team at Thornton & Lowe is experienced in writing plans for businesses across a number of sectors, and have put together the example below. Please use this as a guide only, remembering to always tailor the plan to your client's requirements.
[Placeholder Company Name], with [Number] years of industry experience, is well-equipped to mobilise and deliver exceptional XXX services. We have successfully mobilised numerous contracts from a standing start, as evidenced in [Reference to the figure showcasing successfully mobilised contracts].
Key Tasks and Processes
Timelines, Resources, and Contingencies
Our comprehensive mobilisation plan outlines the timeline and phased deliverables to meet the go-live date of [Insert Date]. [Mobilisation Lead Name] and [Supporting Manager Name], with [Number] and [Number] years of experience respectively, will lead the mobilisation process. We have built contingencies into our plan to account for unforeseen risks/delays.
Equipment and Evidence
We will procure and maintain the required equipment and consumables through our established suppliers. Our equipment list includes [Insert key equipment]. We have successfully mobilised contracts in the past, demonstrating our ability to address challenges and incorporate new sites seamlessly.
Collaboration and Communication
We will collaborate closely with you throughout the mobilisation process, seeking your input and expertise. We will request necessary documentation, meet weekly to discuss progress, and provide written progress reports. Key factors for successful mobilisation include efficient communication, thorough planning, establishing systems and procedures, and staff training.
Contract Start
We will confirm the go-live date, ensure all mobilisation activities are completed on schedule, and communicate with all stakeholders to ensure a smooth transition.
A well-structured mobilisation plan is often a key requirement in tenders, demonstrating your ability to deliver a seamless transition and effective contract start-up. Thornton & Lowe helps businesses create high-quality mobilisation plans that meet buyer expectations and strengthen your bid.
From developing a winning mobilisation plan to supporting your entire bid submission, Thornton & Lowe ensures your tender stands out.
A robust mobilisation plan framework ensures smooth project initiation and execution. It outlines key elements for successful project launch, efficient task allocation, and proactive risk mitigation.
The project plan forms the backbone of your mobilisation strategy. Start by clearly defining the project scope, objectives, and deliverables. Break down the work into manageable tasks and create a detailed timeline for each activity.
Use Gantt charts or project management software to visualise the schedule and dependencies. Identify critical milestones and set realistic deadlines. Consider resource allocation, including personnel, equipment, and materials.
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and success. Include budgeting considerations, outlining estimated costs for each phase of the project. Regularly review and update the plan as needed to ensure it remains relevant throughout the mobilisation process.
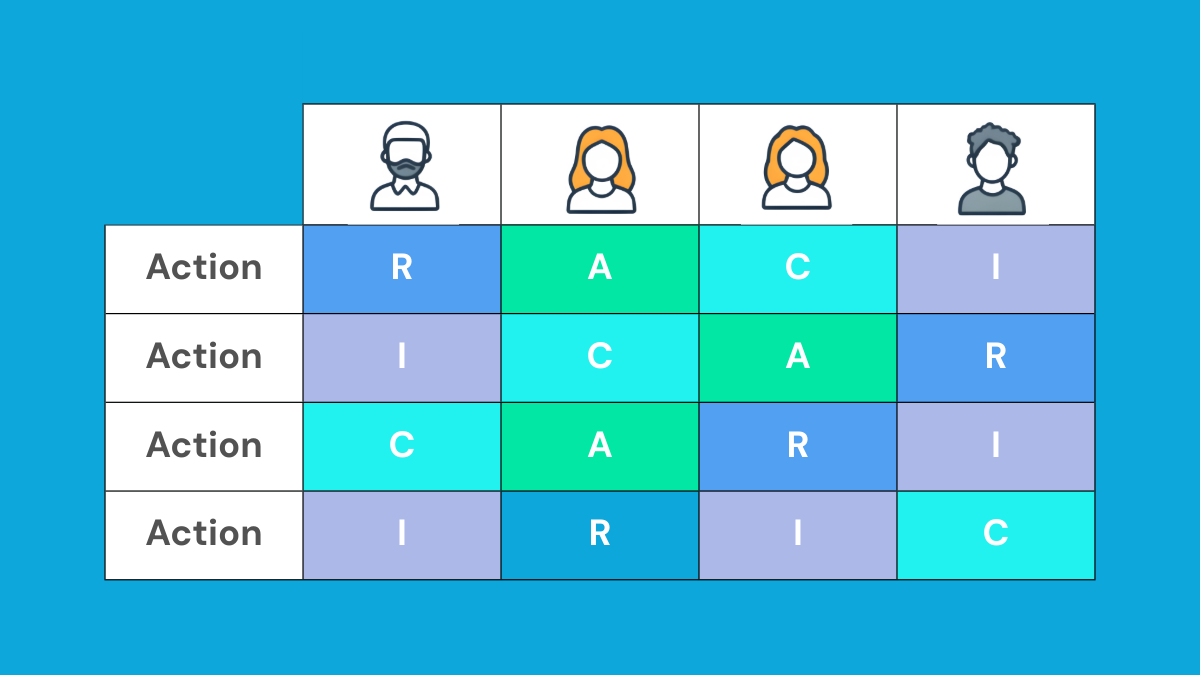
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities are crucial for effective project execution. Create a comprehensive organisational chart outlining the project team structure.
Assign specific tasks and accountabilities to each team member. Define reporting lines and communication channels to ensure smooth information flow. Consider using a RACI matrix (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) to clarify decision-making authority.
Identify any skills gaps within the team and plan for training or external support as needed. Establish a system for regular check-ins and progress updates. Ensure all team members understand their roles and how they contribute to the overall project success.
A comprehensive risk management strategy is essential for anticipating and mitigating potential issues.
Effective pre-mobilisation activities set the foundation for a successful contract implementation. These critical steps ensure all parties are aligned and prepared before the actual mobilisation begins.
A thorough due diligence approach is essential to mitigate risks and identify potential issues. Begin by reviewing all contract documents, including terms, conditions, and scope of work. Verify that all required permits and licences are in place or in progress.
Create a detailed checklist of all contractual obligations and deadlines. This will help you track progress and ensure compliance throughout the mobilisation process.
Assess your current resources and capabilities. Identify any gaps in skills, equipment, or personnel that need to be addressed before mobilisation begins. Consider subcontracting services if necessary to fulfil all contract requirements.
Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential challenges and develop contingency plans. This proactive approach will help you navigate unforeseen issues during mobilisation.
Organise meetings with key stakeholders to establish clear lines of communication and align expectations. These stakeholders may include:
During these meetings, discuss project timelines, milestones, and deliverables. Clarify roles and responsibilities for each party involved in the contract mobilisation.
Create a communication plan outlining how information will be shared throughout the mobilisation process. This should include regular progress updates and a system for addressing concerns or issues as they arise.
Establish a governance structure for decision-making and problem-solving. Clearly define escalation procedures for any conflicts or challenges that may occur during mobilisation.
Review and finalise all contracts, including those with subcontractors and suppliers. Ensure that all terms and conditions align with the main contract and your organisation's policies.
Obtain necessary permissions and approvals from relevant authorities. This may include:
Confirm that all insurance policies are in place and provide adequate coverage for the contract requirements. Update policies if needed to address any specific project risks.
Develop a detailed supplier contract mobilisation plan that outlines key activities, timelines, and responsibilities. Share this plan with all relevant parties to ensure everyone is working towards the same goals.
Establish a system for document control and version management. This will help maintain accurate records throughout the mobilisation process and beyond.
Proper documentation and compliance are crucial for a successful contract mobilisation. These elements ensure transparency, accountability, and adherence to regulatory requirements throughout the project lifecycle.
Effective documentation is essential for minimising potential misunderstandings. Begin by gathering all relevant documents, including the signed contract, project plans, and technical specifications.
Create a centralised repository for easy access and version control. This could be a shared drive or a dedicated project management tool.
Develop a document hierarchy to organise files logically. Use clear naming conventions and folder structures to ensure quick retrieval of information.
Implement a document review and approval process. This helps maintain accuracy and consistency across all project documentation.
Identify all applicable regulatory requirements for your project. This may include industry-specific regulations, data protection laws, and health and safety standards.
Create a compliance checklist to track adherence to these requirements. Regularly review and update this checklist throughout the mobilisation phase.
Assign responsibility for compliance monitoring to a dedicated team member or committee. They should conduct periodic audits to ensure ongoing conformity.
Consider engaging legal counsel or compliance experts for complex regulatory matters. Their expertise can help navigate intricate compliance landscapes.
Establish a comprehensive contract register to track all agreements related to the project. Include key details such as:
Regularly update the register to reflect any changes or amendments to contracts. This ensures you always have an accurate overview of contractual commitments.
Implement a system for tracking contract expiry dates and renewal options. Set up automated alerts to notify relevant stakeholders of upcoming deadlines.
We're here to help with mobilisation plans, tender responses and more.
Contact usEffective operational planning and execution are crucial for successful project mobilisation. These elements ensure smooth implementation and set the stage for achieving project objectives.
A project handbook serves as a central resource for all project-related information. Start by outlining the project scope, objectives, and key deliverables. Include detailed roles and responsibilities for team members and stakeholders.
Add contact information for all relevant parties and emergency procedures. Document project timelines, milestones, and critical paths. Include quality control measures and reporting protocols.
Ensure the handbook covers risk management strategies and mitigation plans. Incorporate health and safety guidelines specific to your project. Update the handbook regularly to reflect any changes or new information.
An impact schedule outlines the sequence of activities and their effects on project progress. Begin by identifying all tasks required for project completion. Estimate the duration of each task and determine dependencies between activities.
Use project management software to create a Gantt chart or network diagram. Highlight critical path activities that directly impact the project timeline. Include resource allocation details for each task.
Establish clear milestones and deadlines for key deliverables. Factor in potential delays and include buffer time where necessary. Review and update the impact schedule regularly to ensure accuracy.
Method statements provide step-by-step instructions for carrying out specific project tasks. Start by identifying high-risk or complex activities that require detailed guidance. Consult with experienced team members to gather best practices and safety considerations.
Write clear, concise instructions for each step of the process. Include required tools, equipment, and personal protective gear. Highlight potential hazards and necessary precautions.
Incorporate relevant safety regulations and industry standards. Use diagrams or flow charts to illustrate complex procedures. Review and update method statements periodically to reflect improvements or changes in processes.
Effective logistics and resource management are crucial for a successful mobilisation plan. This involves securing necessary equipment, planning timelines, and coordinating with subcontractors.
Start by identifying all types of resources needed, including personnel, budget, and materials. Create a detailed inventory list of required equipment and facilities. Consider factors like quantity, specifications, and availability.
Develop a procurement strategy that balances cost-effectiveness with quality. Research potential suppliers and compare their offerings. Negotiate contracts and delivery schedules to ensure timely arrival of resources.
Set up a system to track and manage procured items. This could include asset tagging and a digital inventory management tool. Plan for storage and maintenance of equipment to keep it in optimal condition throughout the project.
A Gantt chart is an essential tool for visualising project timelines. Begin by breaking down the project into specific tasks and milestones. Estimate the duration of each task and identify dependencies between them.
Use project management software to create your Gantt chart. Input tasks, durations, and dependencies. Assign resources to each task and set realistic start and end dates.
Include key milestones and performance targets in your chart. Colour-code tasks based on priority or department for easy visual reference. Regularly update the chart as the project progresses to reflect any changes or delays.
Identify which services need to be subcontracted. Create a detailed scope of work for each subcontracted service, clearly outlining expectations and deliverables.
Develop a rigorous selection process for subcontractors. Evaluate potential partners based on expertise, past performance, and cost-effectiveness. Conduct thorough background checks and request references.
Draft comprehensive contracts that include clear terms, timelines, and quality standards. Establish a communication protocol to ensure smooth coordination between your team and subcontractors.
Implement a monitoring system to track subcontractor performance. Set up regular check-ins and progress reports. Be prepared to address any issues promptly to maintain project momentum.
When creating a contract mobilisation plan, you must carefully consider the financial aspects. Start by reviewing your budget and ensuring it aligns with the project's scope.
Identify all potential costs associated with mobilisation, including:
Create a detailed cash flow forecast to anticipate your financial needs throughout the mobilisation period. This will help you avoid unexpected shortfalls.
Consider securing a line of credit or arranging financing options to cover initial expenses. Many projects require upfront investments before payments start flowing in.
Establish clear payment terms and schedules with your client. Ensure these are documented in the contract to prevent misunderstandings later on.
Set up a system for tracking expenses and invoicing. This will help you maintain accurate financial records and manage your cash flow effectively.
Don't forget to account for contingencies in your budget. Unexpected costs often arise during mobilisation, so it's wise to have a financial buffer.
Effective monitoring and control mechanisms are crucial for ensuring a smooth mobilisation process. These practices help identify potential issues early and keep the project on track.
To effectively monitor implementation work, establish clear procedures and guidelines. Create a detailed checklist outlining key tasks and responsibilities for each team member. This helps ensure nothing is overlooked during the mobilisation phase.
Set up regular progress meetings to review completed tasks and address any challenges. Implement a master programme plan that includes timelines, resource allocation, and cost estimates for the implementation phase.
Utilise project management software to track task completion and dependencies. This allows you to easily visualise progress and identify potential bottlenecks.
Consider implementing a change management process to handle any unexpected modifications to the original plan. This ensures that changes are properly evaluated and approved before implementation.
Define clear, measurable success metrics at the outset of your mobilisation plan. These key performance indicators (KPIs) should align with your overall project objectives.
Establish a baseline for each metric and set realistic targets. Common KPIs for mobilisation include:
Implement a robust reporting system to track these metrics regularly. Use visual dashboards to present data in an easily digestible format for stakeholders.
Conduct periodic reviews to assess progress against your KPIs. Be prepared to adjust your approach if certain metrics are falling short of expectations.
Speak to Thornton & Lowe's bid writing experts today.
Get in touchMade by Statuo



